Matter In Our Surroundings
What is distance-time graph of a body? Draw distance-time graphs for,
(i) a stationary body,
(ii) a body moving with uniform velocity, and
(iii) a body moving with variable velocity.
Distance-time graph:
It is a graph obtained by plotting distance travelled along Y-axis and time taken along X-axis.
(i) Distance-time graph for stationary body:
The position of a stationary body does not change with time. So distance-time graph for a stationary body is a straight line parallel to time axis, as shown in Fig. 8.7 (a).
(ii) Distance-time graph for uniform velocity:
For a body moving with uniform velocity, the distance travelled is proportional to the time taken. So distance-time graph is a straight line inclined to the time axis, as shown in Fig. 8.7 (b).
(iii) Distance-time graph for variable velocity:
When a body moves with variable velocity, it covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time. So the distance-time graph is not a straight line but it is a curve, as shown in Fig. 8.7 (c).
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Matter In Our Surroundings Chapter
Give reason for the following observations.
Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
Give reason for the following observations.
We can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
What is the physical state of water at
a) 25°C
b)00C
c)1000C
What is the physical state of water at
0°C
What is the physical state of water at
100°C
Give two reasons to justify
Water at room temperature is a liquid.
Give two reasons to justify
An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Why is ice at 273K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature ?
What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam ?
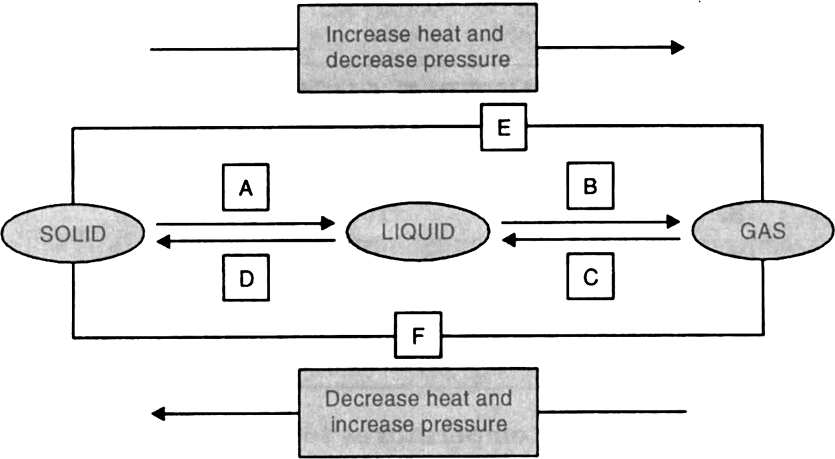
8. Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing state change :
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area