Spatial Information Technology
Discuss raster and vector data formats. Give examples.
Raster data represents a graphic feature as a pattern of grids of squares whereas Vector data represents the object as a set of lines drawn between specific points. Consider a line drawn diagonally on a piece of paper. A Raster file would represent this imagery subdividing the paper into a matrix of small rectangles similar to a sheet of paper called cells. Each cell is assigned a position in the data file and given a value based on the attribute of that position. Its row and column coordinates may identify any individual pixel.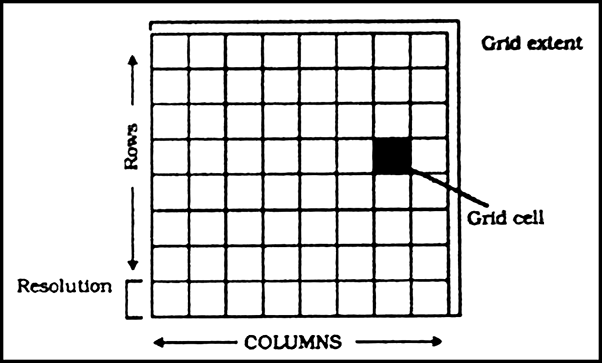
Fig: Generic Structure for a Grid
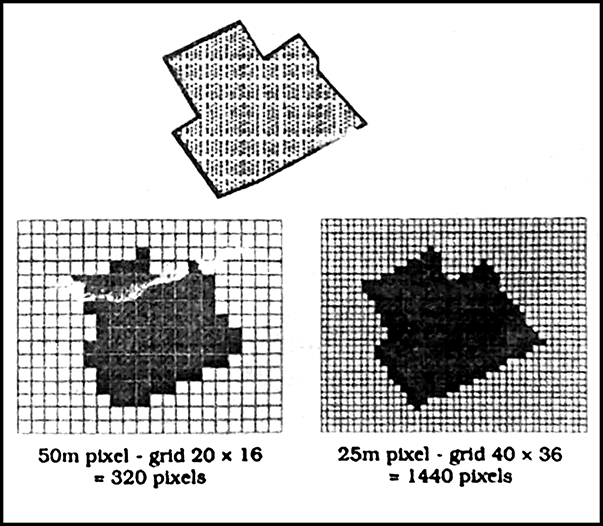
Fig: Effect of Grid Size on Data in Raster Format
Vector Format: A Vector representation of the same diagonal line would be record the position of the line by simply recording the coordinates of its starting and ending points. Each point would be expressed as two or three members depending on whether the representation was 2D or 3D often referred to as XY or XYZ co-ordinates.
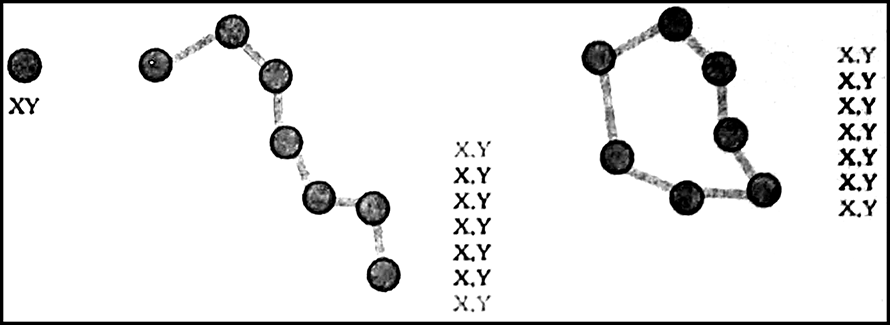
Fig: The Vector Data Model is based around coordinates pairs.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Spatial Information Technology Chapter
Differentiate between Raster and Vector data models
What is an overlay analysis?
What are the advantages of GIS over manual methods?
What are important components of GIS?
What are different ways in which spatial data is built in GIS core?
What is spatial information technology?
Discuss raster and vector data formats. Give examples.
Write an explanatory account of the sequence of activities involved in GIS related work.
What is GIS?
What are the main types of GIS?
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area