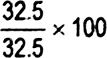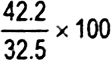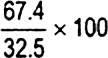Data : Its Source And Compilation
What is the importance of an index number? Taking an example examine the process of calculating an index number and show the changes.
An index number is a statistical measure designed to show changes in variable or a group of related variables with respect to time, geographic location or other characteristics. It is to be noted that index numbers not only measure changes over a period of time but also compare economic conditions of different locations-industries, cities or countries. Index number is widly used in economics and business to see changes in price and quantity. There are various methods for the calculations of index number. Simple aggregate method is most commonly used. It is obtained using the following formula: 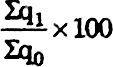
Σq1 = Total of the current year production.
Σq0 = Total of the base year production.
Example: Production of iron ore in India.
|
Year |
Production (in million tonnes) |
Calculation |
Index Number |
|
1970-71 |
32.5 |
|
100 |
|
1980-81 |
42.2 |
|
130 |
|
1990-91 |
53.7 |
|
165 |
|
2000-01 |
67.4 |
|
207 |
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Data : Its Source And Compilation Chapter
Enumerate five sources of secondary data.
Discuss the national and international agencies where from secondary data may be collected.
What is the importance of an index number? Taking an example examine the process of calculating an index number and show the changes.
In a class of 35 students of geography following marks were obtained out of a 10 mark unit text - 1, 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 2, 3, 4, 0, 2, 5, 8, 4, 5, 3, 6, 3, 2, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 7, 8, 9, 7, 9, 4, 5, 4, 3. Represent the data in the form of a group frequency distribution.
Collect the last test result of Geography of your class and represent the marks in the form of a group frequency distribution.
What do you mean by data? Describe the different sources of collecting data.
What is meant by tabulation of data?
Describe the main steps of Data Analysis.
What are the main steps involved in data classification?
Define data.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area