The p-Block Elements
(a) Draw the structures of the following molecules:
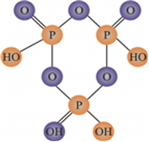
(i) (HPO3)3
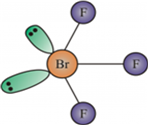
(ii) BrF3
(b) Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) HgCl2 + PH3-->
(ii) SO3 + H2SO4 -->
(iii) XeF4 + H2O -->
OR
(a) What happens when?
(i) Chlorine gas is passed through a hot concentrated solution of NaOH?
(ii) Sulphur dioxide gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a Fe (III) salt?
(b) Answer the following:
(i) What is the basicity of H3PO3 and why?
(ii) Why does fluorine not play the role of a central atom in inter-halogen compounds?
(iii) Why do noble gases have very low boiling points?
(i) (HPO3)3
(ii) BrF3 has a bent T-shape and can be drawn as follows.
(b)
(i) 3 HgCl2 + 2 PH3 --> Hg3P2 + 6 HCl
(ii) SO3 + H2SO4 ---> H2S2O7
(iii) 6 XeF4 +12 H2O ---> 4Xe + 2 XeO3 + 24 HF + 3O2
Or
(a)
(i) When chlorine is passed through a hot concentrated solution of NaOH, it undergoes disproportionation in which chlorine is simultaneously reduced to Cl-and is oxidised to
3Cl2 + 3NaOH --> 5NaCl + NaClO3 + 3H2O
(ii) SO2 acts as a reducing agent when passed through an aqueous solution containing Fe(III) salt. It reduces Fe(III) to Fe(II) i.e., ferric ions to ferrous ions.
2Fe3+ + SO2 + 2H2O ---> 2Fe2+ + SO42-+ 4H+
(b)
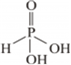
(i) Basicity of H3PO3 depends upon the number of ionizable -OH groups present in the molecule. That is the number of hydrogen attached to the electronegative atom oxygen.
H3PO3 has two ionizable –OH group, thus its basicity is 2
The structure of H3PO3 follows as:
(ii) Fluorine does not play the role of a central atom in inter-halogen compounds because of the absence of d- orbital. Also, because of the small size of fluorine, it cannot accommodate larger halogen groups.
(iii) The noble gases have low boiling point due to the fact that the noble gases are mono atomic. Having no interatomic forces except weak dispersion forces.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From The p-Block Elements Chapter
Write a balanced equation for the hydrolytic reactions PCl5 in heavy water.
What is the basicity of H3PO4?
What happens when H3PO3 is heated?
List the important source of sulphur.
Write the order of thermal stability of the hydrides of Group 16 elements.
Why is H2O a liquid and H2S a gas?
Which of the following does not react with oxygen directly?
Zn, Ti, Pt, Fe
Complete the following reactions
(i) C2H4 + O2 →
(ii) 4Al + 3O2 →
Why does O3 act as a powerful oxidising agent?
How is O3 estimated quantitatively?
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area