Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Question
Write the mechanism of the reaction of HI with methoxymethane.
Answer
Mechanism: The cleavage of ethers by halogen acids occur by the following mechanism.
Step 1. Ethers being Lewis basis, undergo protonation to form oxonium salts:
Step 2. The protonated ether thus formed undergoes nucleophilic attack by the halide ion to form a molecule of an alkyl halide and a molecule of an alcohol.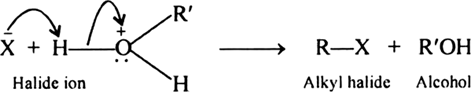
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Chapter
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system.
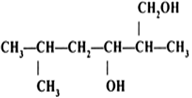
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system.
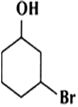
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system.
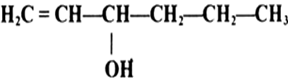
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system.
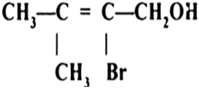
Show how are the following alcohols prepared by the reaction of a suitable Grignard reagent on methanal?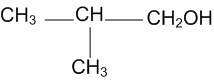
Show how are the following alcohols prepared by the reaction of a suitable Grignard reagent on methanal?

Write structures of the products of the following reactions:
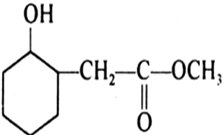
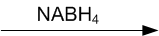
Write structures of the products of the following reactions:
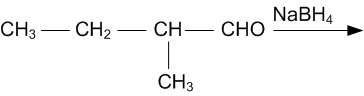
Give structures of the products you would expect when each of the following alcohol reacts with,
(a) HCl—ZnCl2 (b) HBr and (c) SOCl2.
(i) Butan-1-ol (ii) 2-Methyl butan-2-ol.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area