Hydrocarbons
How will you explain the directive influence of halogens?
Halogens (Cl, Br, l) contain three pairs of electrons and thus release electrons to the aromatic ring through resonance. But due to its electrons withdrawing (-Inductive effect) nature, it also intensifies the positive charge on carbocation. Thus, inductive effect and resonance effect work in the opposite direction and the result of two opposing effects is electron withdrawal. That is why halogens deactivate the aromatic ring for electrophilic substitution. Consider chloro-benzene.+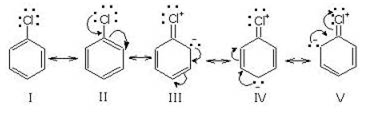
Thus chlorine atom deactivates the ring due to -I effect and directs the incoming electrophile to attack at the ortho and para position due to resonance effect.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Hydrocarbons Chapter
Out of n-pentane, isopentane and neopentane which has lower boiling point?
During the pyrolysis of alkanes C-C bonds break in preference to C-H bond. Why?
Define cracking.
What is the function of iodic acid in the iodination of alkanes? Can we use any other substance in its place?
What is alternation effect?
Arrange the following compounds in order of their increasing boiling points:
n-Pentane, n-Hexane, Ethane, 2-2-Dimethylpentane, 2-Methylpentane.
Why is light or heat necessary to initiate chlorination reaction of alkanes?
What are conformation or rotational isomers?
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area