Hydrocarbons
Why do alkynes undergo electrophilic addition reactions ?
The electrophilic addition reactions take place in alkynes due to the presence of high electron density in the triple bond. This means that – C ≡ C – can act as a source of electrons. There are certain reagents (electrophiles) which are capable of adding to alkyne molecules forming an addition compound. Since such reactions are initiated by the electrophiles and hence are known as electrophilic addition reactions.
The addition product further reacts with E-Nu (attacking reagent) to form addition product i.e. alkane derivative.
Mechanism: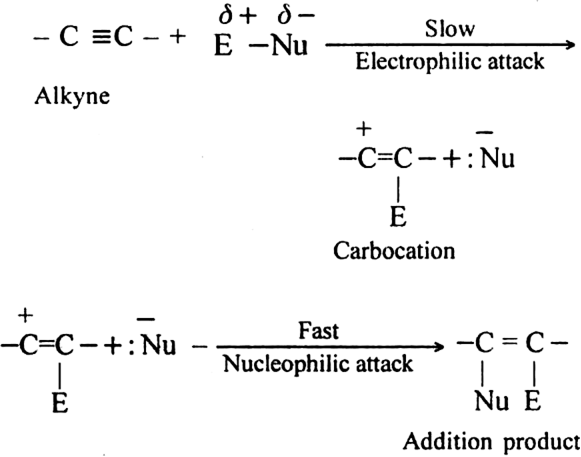
The electrophilic addition gets repeated and alkene derivative changes to alkane derivative.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Hydrocarbons Chapter
What is the function of iodic acid in the iodination of alkanes? Can we use any other substance in its place?
What is alternation effect?
Arrange the following compounds in order of their increasing boiling points:
n-Pentane, n-Hexane, Ethane, 2-2-Dimethylpentane, 2-Methylpentane.
Why is light or heat necessary to initiate chlorination reaction of alkanes?
What are conformation or rotational isomers?
Out of eclipsed and staggered conformation of ethane, which is more stable?
Can you separate the two conformations of ethane?
Why are alkenes called olefins?
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area