Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Explain the principle of paper chromatography.
The analysis of unknown substances by the flow of solvent on a filter paper is known as paper chromatography. This technique proceeds by a mechanism which is partly partition (distribution) and partly adsorption. The constituents of a mixture are distributed between the water held in the filter paper (water thus acts as a stationary phase) and an organic solvent (mobile phase).
In this method, a drop of the test solution is applied as a small spot near one edge of the filter paper and spot is dried. When the end of the paper strip is dipped into a developing solvent, the solvent rises up the paper by capillary action and flows over the spot. The paper selectively retains different components according to their differing partition in the two phases. The paper strip so developed is known as a chromatogram. The spots of the separated coloured compounds are visible at different heights from the position of the initial spot on the chromatogram. The spots of the separated colourless compounds may be made visible either by ultraviolet light or by the use of a suitable spray reagent.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques Chapter
What are isomers?
How many chain isomers are possible for pentane?
Which characteristic is common to different isomers of a compound?
Name three alkanes which do not show chain isomerism.
Name the types of structural isomerism shown by alkanes.
Name the four main types of structural isomerism.
Write the three possible open chains of five carbon atoms
What types of structural isomerism is shown by the following pairs of organic compounds ?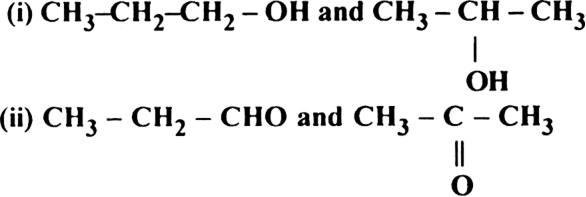
Write the tautomer of acetaldehyde and write its IUPAC name.
Draw the structure of the tautomer of phenol and write its IUPAC name.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area