Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Give a brief description of the principles of the following techniques taking an example in each case.
(a) Crystallisation (b) Distillation
(c) Chromatography
Crystallisation:
This is a most common method for the purification of solid organic compounds. It is based on the fact that certain organic compounds are partly soluble in a solvent at room temperature and solubility increases with increases in temperature. Example: separation of sugar from a mixture of sugar and common salt by using ethanol.
Distillation:
This method is based on the principle that at constant pressure every pure liquid boils at a definite temperature called its boiling point. The method is used for the purification of those liquids which boil without decomposition provided the impurities are non-volatile. The method is applied for the purification when the two liquid differs in the boiling points by 30-50K.
Chromatography
The technique dependes on the distribution of the mixture between two phases, one fixed and the other mobile. The fixed phase may bean absorbent column (a solid chemical compound) or a paper strip. The moving phase may be a liquid or gas. the mixture to be separted is dissolved in the moving phase and passed over the fixed phase. There are three types of chromatography.
i) adsorption chromatography
ii) partition chromatography
iii) gas chromatography
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques Chapter
What does IUPAC stand for?
What system of nomenclature is accepted universally?
What are isomers?
How many chain isomers are possible for pentane?
Which characteristic is common to different isomers of a compound?
Name three alkanes which do not show chain isomerism.
Name the types of structural isomerism shown by alkanes.
Name the four main types of structural isomerism.
Write the three possible open chains of five carbon atoms
What types of structural isomerism is shown by the following pairs of organic compounds ?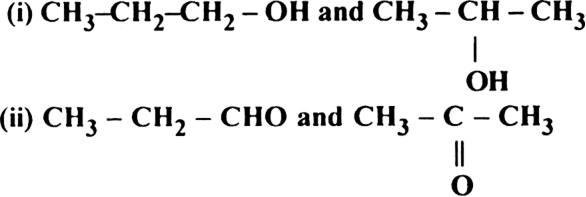
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area