Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Discuss the rules for IUPAC nomenclature of compounds containing one functional group, multiple bonds and substituents.
(A) Lowest number for the functional group.
Rule. 1. Select the longest continuous chain containing the carbon atom having the functional group. e.g.
Rule 2. The numbering of atoms in the parent chain is done in such a way that the lowest number must be always given to the functional group e.g.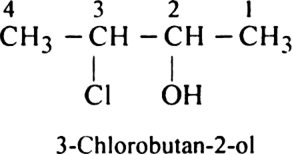
Rule 3. All the rules for naming side chains as substituents are then followed as in the case of alkanes.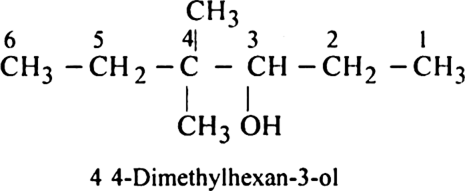
Rule 4. When a chain containing functional groups such as –CHO, – COOH, –COOR, – CONH2, –COCl, –C ≡ N etc. is present it is always given number 1 and number l is usually omitted from the final name of the compound.
Rule 5. If the organic compound contains a functional group, multiple bond, side chain or substituent, the following order of preference should be followed:
Functional group > Double bond or Triple bond > Substituent/side chain, e.g.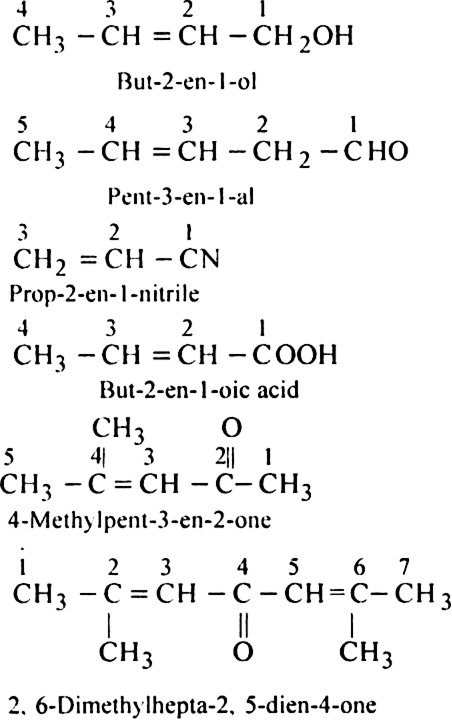
Rule 6. If the compound contains two or more like groups, the numerical prefixes di, tri, tetra etc. are used and the terminal ‘e’ from the primary suffix is retained.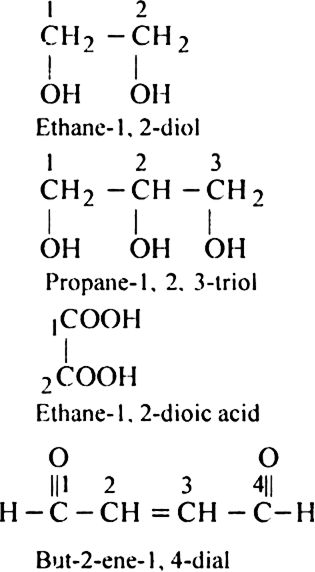
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques Chapter
What system of nomenclature is accepted universally?
What are isomers?
How many chain isomers are possible for pentane?
Which characteristic is common to different isomers of a compound?
Name three alkanes which do not show chain isomerism.
Name the types of structural isomerism shown by alkanes.
Name the four main types of structural isomerism.
Write the three possible open chains of five carbon atoms
What types of structural isomerism is shown by the following pairs of organic compounds ?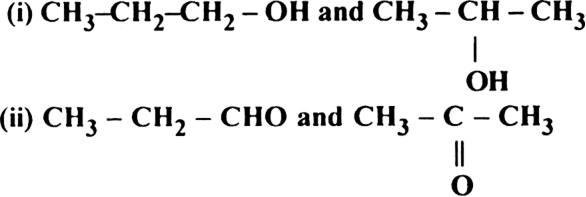
Write the tautomer of acetaldehyde and write its IUPAC name.
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area