Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques
What do you understand by:
(i) Isomerisation reaction
(ii) Condensation reaction?
(i) Isomerisation reaction. All those reactions in which interconversion of isomers take place without affecting the molecular formulae and carbon skeletons of reactants and products are called Isomerisation reactions. For example,
(ii) Condensation reaction. All those reactions in which two same or different organic reactants unite to give a product with or without the elimination of another, simple molecule are called condensation reaction. For example condensation of aldehyde or ketone.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques Chapter
What does IUPAC stand for?
What system of nomenclature is accepted universally?
What are isomers?
How many chain isomers are possible for pentane?
Which characteristic is common to different isomers of a compound?
Name three alkanes which do not show chain isomerism.
Name the types of structural isomerism shown by alkanes.
Name the four main types of structural isomerism.
Write the three possible open chains of five carbon atoms
What types of structural isomerism is shown by the following pairs of organic compounds ?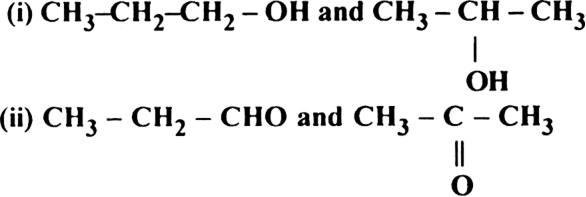
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area