Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Describe briefly the rules for writing the IUPAC names of long chain hydrocarbons.
The following rules are used for naming the branched chain alkanes:
Rule 1. The largest possible straight chain of carbon atoms in the molecule is chosen. The molecule is then named as the derivative of this hydrocarbon.
Rule 2. If two chains of equal lengths are possible, select the one with a large number of side chains.
Named as hexane with one alkyl substituent (Wrong).
Rule 3. Number the carbon atoms in the selected chain so that the functional group or substituent is given the lowest possible number. The number that indicates the position of the substituent or side chain is called locant.
Rule 4. Also if there are two or more than two substituents in the chain, then numbering is done in such a manner that the sum of locants is lowest. This rule is also called lowest sum rule.
Rule 5. In the case of more than one identical alkyl substituents prefixes, di-, tri-, tetra etc are used to indicate whether there are two, three, four, etc. substituents.
Rule 6. When two or more chains of different nature are present, each is denoted by a number, keeping in mind Rules NO. 2 and 3. These are named in alphabetical order.
Rule 7. In case two or more substituents of different nature are attached to the chain. These should be arranged alphabetically. While doing so prefixes di- and tri- are not considered. For example.
Rule 8. If two similar substituents lie at equal distances from the ends of the chain, then numbering should be done from either side e.g.
Rule 9. If two similar substituents lie at equal distances from the ends of the chain, the chain is numbered from the end where there are more branches. e.g.,
Rule 10. If two, unlike substituents, are at equal distances from the ends of the chain, then the numbering of the chain is done in such a way that the group which comes first in the alphabetical order (written first in the name) gets a lower number.
Rule 11. In case the substituent on the parent chain is complex, it is named as a substituted alkyl group by numbering the carbon atom of this group attached to the parent chain as I. The name of such substituent is given in brackets in order to avoid confusion with the numbering of the parent chain.
Rule 12. While writing the trivial names of the substituent in alphabetical order, the prefixes iso-and neo- are considered to be the part of the fundamental name of the alkyl group. The prefixes second tert- are not considered to be the part of the fundamental name.
Prefix-sec is not considered as a part of name while-iso is considered.
Rule 13. If there happen to be two chains of equal size, then that chain is to be selected which contains a number of the side chains. After selection of the chain, numbering is to be done from the end closer to the substituent.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques Chapter
How many chain isomers are possible for pentane?
Which characteristic is common to different isomers of a compound?
Name three alkanes which do not show chain isomerism.
Name the types of structural isomerism shown by alkanes.
Name the four main types of structural isomerism.
Write the three possible open chains of five carbon atoms
What types of structural isomerism is shown by the following pairs of organic compounds ?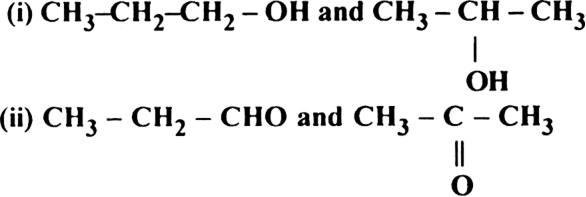
Write the tautomer of acetaldehyde and write its IUPAC name.
Draw the structure of the tautomer of phenol and write its IUPAC name.
Define ring - chain isomerism. Given one example.?
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
NCERT Book Store
NCERT Sample Papers
Sponsor Area