Sponsor Area
Ray Optics And Optical Instruments
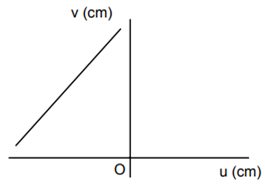
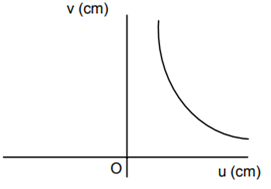
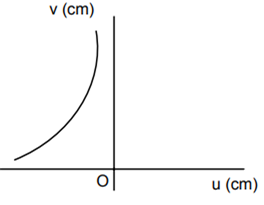
A student measures the focal length of the convex lens by putting an object pin at a distance ‘u’ from the lens and measuring the distance ‘v’ of the image pin. The graph between ‘u’ and ‘v’ plotted by the student should look like
C.
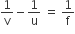
Some More Questions From Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Chapter
In an optics experiment, with the position of the object fixed, a student varies the position of a convex lens and for each position, the screen is adjusted to get a clear image of the object. A graph between the object distance u and the image distance v, from the lens, is plotted using the same scale for the two axes. A straight line passing through the origin and making an angle of 45o with the x-axis meets the experimental curve at P. The coordinates of P will be
An experiment is performed to find the refractive index of glass using a travelling microscope. In this experiment distance are measured by
Two lenses of power -15D and +5D are in contact with each other. The focal length of the combination is
The angle of incidence at which reflected light totally polarized for reflection from air to glass (refractive index n), is
If θ1 and θ2 be the apparent angles of dip observed in two vertical planes at right angles to each other, then the true angle of dip θ is given by
A beam of light from a source L is incident normally on a plane mirror fixed at a certain distance x from the source. The beam is reflected back as a spot on a scale placed just above the source L. When the mirror is rotated through a small angle θ, the spot of the light is found to move through a distance y on the scale. The angle θ is given by
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series