Sponsor Area
Ray Optics And Optical Instruments
Obtain the mirror formula and write the expression for the linear magnification.
A relationship among the object distance (u), the image distance (v) and the focal length (f) of a mirror are called the mirror formula.
The formula is given by
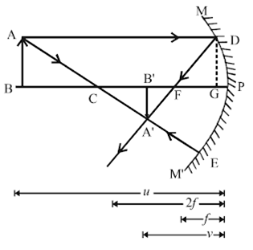
Take an object AB beyond C of a concave mirror MM'. A ray AD parallel to principal axis passes through focus after reflection.
Another ray AE which is passing through C comes back along the same path after reflection.
These two reflected rays intersect at A'. A' draw perpendicular A'B' on the principal axis. So A'B' is a real and inverted image which is formed between C and F which is smaller than the object in size.
Draw DG perpendicular to the principal axis. So, applying sign convention, we get
PB = - u,
PB' = -v
PF = -f
PC = -2f
Now, In △ABC and △A'B'C, ∠ABC =∠A'B'C = 90°
∠ACB = ∠A'CB' (Vertically Opposite angles)
∴ △ABC ~△A'B'C (AA similarity)
(the corresponding side of similar triangles are in proportion)..... (1)
In △DGF and △A'B'F, ∠DGF = ∠A'B'F = 90°
∠DGF= ∠A'FB' (vertically opposite angles)
△DGF ~△A'B'F (AA similarity)
(corresponding sides of similar triangles are in proportion)
But AB = DG (the perpendicular distance between two parallel lines are equal)
Let us assume the mirror is very small,
∴ G and P are very close to each other so that GF = PF.
From equation (3),
If the mirror is plane, the size of the image is always equal to the size of the object i.e., magnification is unity. But the case is different for a curved mirror. The size of the image is different from the size of the object in such a 'mirror'. The image may be greater or smaller in size than the object depending upon the nature of the mirror or the location of the object.
Let I and O be the size of the image and the object respectively. The ratio I/O is called magnification, and it is denoted by m.
Magnification, m = I/O = -v/u
This is called linear magnification.
Some More Questions From Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Chapter
Explain two advantages of a reflecting telescope over a refracting telescope.
In an optics experiment, with the position of the object fixed, a student varies the position of a convex lens and for each position, the screen is adjusted to get a clear image of the object. A graph between the object distance u and the image distance v, from the lens, is plotted using the same scale for the two axes. A straight line passing through the origin and making an angle of 45o with the x-axis meets the experimental curve at P. The coordinates of P will be
An experiment is performed to find the refractive index of glass using a travelling microscope. In this experiment distance are measured by
Two lenses of power -15D and +5D are in contact with each other. The focal length of the combination is
The angle of incidence at which reflected light totally polarized for reflection from air to glass (refractive index n), is
If θ1 and θ2 be the apparent angles of dip observed in two vertical planes at right angles to each other, then the true angle of dip θ is given by
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





