(i) Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons.
(ii) How does drift velocity of electrons in a metallic conductor vary with increase in temperature ? Explain.
i) Expression for the drift velocity of electrons:
When a potential difference is applied across a conductor, an electric field is produced and free electrons are acted upon by an electric force (=-eE).
As a result, electrons accelerate and keep colliding with each other and acquire a constant average velocity (vd).
Therefore,
Fe = -Ee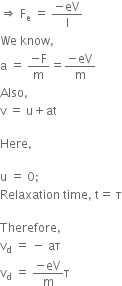
ii) As the temperature is increased, drift velocity of electrons in a metallic conductor increases.
From the above relation,
Therefore, as the temperature of the metallic conductor increases, the collision between the electrons and ions increases, resulting in decrease in the relaxation time.
Thus, the drift velocity decreases.



