Question
A travelling harmonic wave on a string is described by:
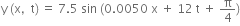
(a) What are the displacement and velocity of oscillation of a point at x = 1 cm, and t = 1 s? Is this velocity equal to the velocity of wave propagation?
(b) Locate the points of the string which have the same transverse displacements and velocity as the x =1 cm point at t = 2 s, 5 s and 11 s.
Solution
(a) The given harmonic wave is:

k = 2π/λ
∴ λ = 2π/k
and,
ω = 2πv
Therefore,
v = ω/2π
Speed, v = vλ = ω/k
where,
ω = 12rad/s
k = 0.0050 m-1
Therefore,
v = 12/0.0050 = 2400 cm/s
Hence, the velocity of the wave oscillation at x = 1 cm and t = 1s is not equal to the velocity of the wave propagation.
(b) Propagation constant is related to wavelength as,
k = 2π/λ
∴ λ = 2π/k = 2 × 3.14 / 0.0050
= 1256 cm = 12.56 m \
Therefore, all the points at distance nλ (n = ±1, ±2, .... and so on), i.e. ± 12.56 m, ± 25.12 m, … and so on for x = 1 cm, will have the same displacement as the x = 1 cm points at t = 2 s, 5 s, and 11 s.

= 90 coss (732.81°) = 90 cos (90 × 8 + 12.81°)
= 90 cos (12.81°)
= 90 × 0.975 =87.75 cm/s
Now, the equation of a propagating wave is given by,
y (x, t) = asin (kx + wt + Φ)
where, k = 2π/λ
∴ λ = 2π/k
and,
ω = 2πv
Therefore,
v = ω/2π
Speed, v = vλ = ω/k
where,
ω = 12rad/s
k = 0.0050 m-1
Therefore,
v = 12/0.0050 = 2400 cm/s
Hence, the velocity of the wave oscillation at x = 1 cm and t = 1s is not equal to the velocity of the wave propagation.
(b) Propagation constant is related to wavelength as,
k = 2π/λ
∴ λ = 2π/k = 2 × 3.14 / 0.0050
= 1256 cm = 12.56 m \
Therefore, all the points at distance nλ (n = ±1, ±2, .... and so on), i.e. ± 12.56 m, ± 25.12 m, … and so on for x = 1 cm, will have the same displacement as the x = 1 cm points at t = 2 s, 5 s, and 11 s.



