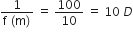Question
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus.
(b) In the above ray diagram, mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper signs (+ve or –ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case.
(c) Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification –1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre.
Solution
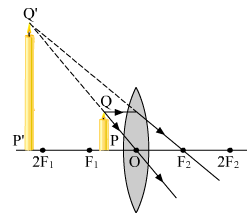
a)
When an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus, the image is formed beyond 2F1 (on the same side of the object), and the ray diagram is obtained is as follows:
 b)
b) The object distance (u) and the image distance (v) are as shown below. Since both the image and the object lie in a direction opposite to the direction of incoming rays, the magnitude will be negative for both.
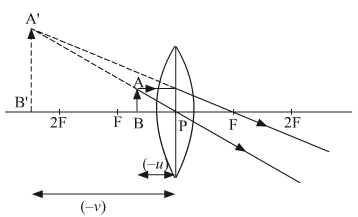
The relation between u, v and f is given by the lens formula,

c)
Given,
u = -20 cm
m = -1
Since magnification is given as,

Focal length (f) can be calculated as:
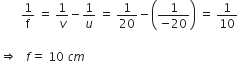
Thus, the power of the convex lens,
P =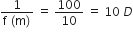

c)
Given,
u = -20 cm
m = -1
Since magnification is given as,

Focal length (f) can be calculated as:
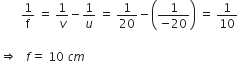
Thus, the power of the convex lens,
P =