State the rules used for drawing images formed by spherical lenses.
Rules for image formation by spherical lenses:
The position of the image formed by any spherical lens can be found by considering any two rays of light coming from a point on the object.
(i) A ray from the object, parallel to the principal axis, after refraction passes through the second principal focus F2 [in a convex lens, as shown in Fig.(a)] or appears to diverge [in a concave lens, as shown in Fig.(b)] from the first principal focus F1.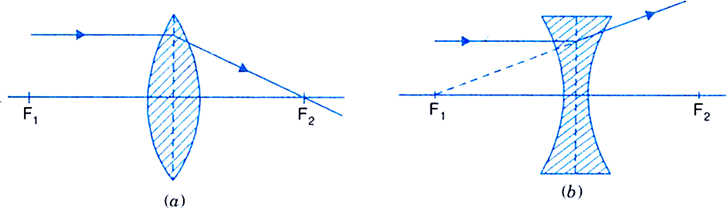
Fig. Path of ray incident parallel to the principal axis of (a) convex lens (b) concave lens.
(ii) A ray of light passing through the first principal focus [in a convex lens, as shown in Fig. (a)] or appearing to converge at the focus [in a concave lens, as shown in (b)] emerges parallel to the principal axis after refraction. 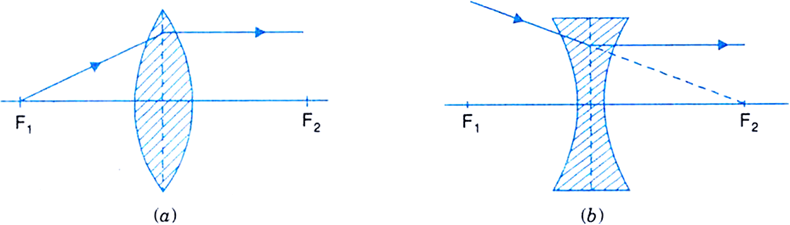
Fig. Path of a ray passing through focus of (a) convex lens (b) concave lens
(iii) A ray of light, passing through the optical centre of the lens, after refraction, emerges without any deviation. The figure below illustrates the ray diagram.
Fig. Path of a ray passing through the optical centre of (a) convex lens (b) concave lens





