With the help of ray diagrams, explain the formation of images by a convex mirror for the following position of the object:
(i) Object between pole and infinity.
(ii) Object at infinity.
(i) Object between pole and infinity: As shown in Fig.(a), an object AB is placed on the principal axis of a convex mirror. A ray AM passing parallel to the principal axis, after reflection, appears to come from the focus F.
The ray AN passing through the centre of curvature C is reflected back along its own path. The two reflected rays appear to come from a common point A' behind the mirror. So A' is the virtual image of A. The line A'B' upon the principal axis is the complete image of AB. Hence a virtual, erect and diminished image is formed behind the mirror between Focus and Pole.
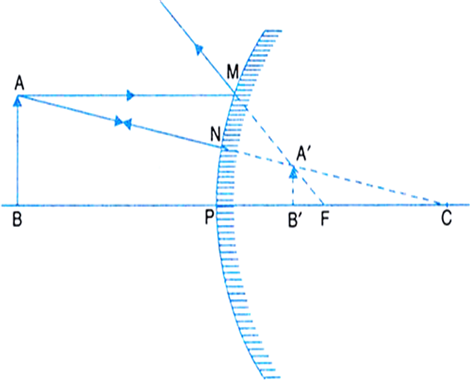
Fig.(a) Image formed by a convex mirror with the object between pole and infinity.
(ii) Object at infinity: When the object is placed at infinity, the incident parallel rays appear to diverge from the focus after reflection from the mirror, as shown in Fig (b). Hence a virtual, erect and extremely diminished image is formed behind the mirror.
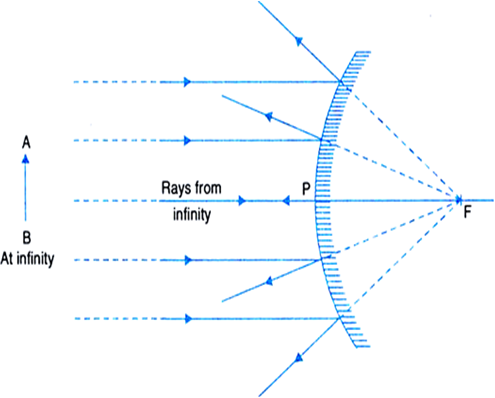
Fig.(b). Image formed by a convex mirror with the object at infinity.
Table. Nature, size a
nd position of images formed by a convex mirror
Position of the object | Position of the image | Nature of the image | Size of the image |
1. Between pole P and infinity | Between P and F, behind the mirror | Virtual and erect | Diminished |
2. At infinity | At the focus, behind the mirror | Virtual and erect | Highly diminished, point-sized |





