Explain the characteristics of sound. On what factors do they depend?
The three characteristics of sound are,
(i) Loudness, (ii) Pitch and (iii) Quality or timbre.
(i) Loudness: The physiological response of the ear to the intensity of sound is called as loudness.
It distinguishes between a loud sound and low sound.
Loudness depends on two main factors:
(a) Intensity of sound which is directly proportional to the square of the amplitude of the sound wave.
(b) Sensitivity of the ear.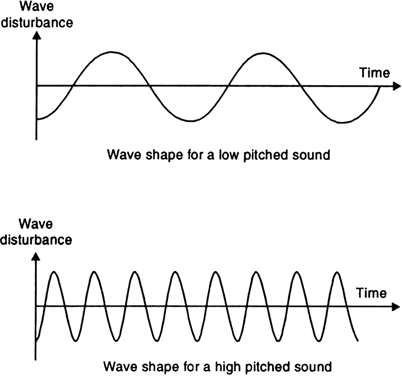
Fig. Soft sound has small amplitude and louder sound has large amplitude. The graph shows the wave shapes of a loud sound and a soft sound of the same frequency.
(ii) Pitch: Pitch is the sensation which helps a listener to distinguish betwen a high and a grave note. Pitch depends on frequency.
The faster the vibration of the source of sound, the higher is the frequency and higher is the pitch.
From the fig. below we can see that a high pitch sound corresponds to more number of compressions and rarefactions passing a given point per unit time.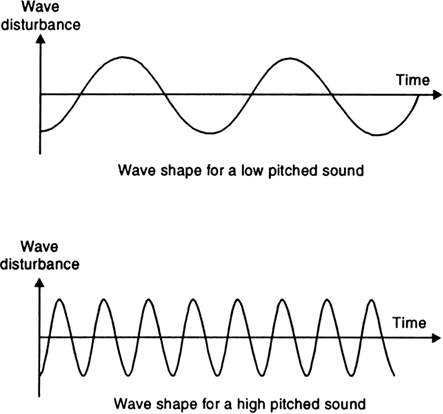
Fig. 12.17. Low pitch sound has low frequency and high pitch sound has high frequency.
(iii) Quality or timbre: The characteristic which enables us, to distinguish one sound from another having the same pitch and loudness is called as the quality or timbre.



