Define the terms amplitude, intensity, time period, frequency, wavelength and velocity of a wave. Give their SI units.
Sound waves are characterised by the following physical quantities:
(i) Amplitude: The maximum displacement suffered by the particles of the medium from their mean positions during the wave propagation is called ‘amplitude’ of the wave.
It is denoted by A.
Its SI unit is metre (m).
Crests and troughs have amplitude A.
(ii) Intensity: The amount of sound energy passing each second through unit area is called the intensity of the sound wave.
Larger the amplitude of a wave, larger is its intensity. In fact.
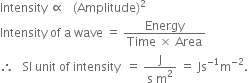
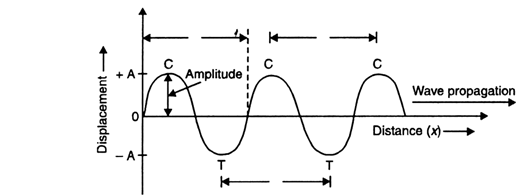
Fig. 12.13. Characteristics of a wave.
(iii) Time period: The time period of a wave is defined as the time in which a particle of the medium completes one vibration to and fro about its mean position.
Time period is equal to the time taken by two successive compressions or rarefactions of a sound wave to cross a fixed point.
It is represented by the symbol T.
Its SI unit is second (s).
(iv) Frequency: The number of waves produced per second is called frequency of the wave.
It is equal to the number of compressions or rarefactions crossing a point per unit time. It is denoted by v (nu).
It is equal to the reciprocal of time period.
Thus,
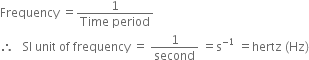
Wavelength: Wavelength is the distance travelled by the wave during the time a particle of the medium completes one vibration.
It is equal to the distance between two successive crests or troughs or between two successive compressions and rarefactions and is denoted by λ (lambda).
Its SI unit is metre (m).
Wave velocity: Wave velocity is the distance travelled by a wave per unit time.
It is the speed with which a disturbance (crest, trough, compression or rarefaction) propagates through a medium.
Its SI unit is ms–1.



