State and explain Newton’ s third law of motion.
Newton’s third law of motion.
According to Newton's third law, to every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
When one objects exerts a force (action) on another object, then the second object also exerts a force (reaction) on the first.
These two forces are always equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.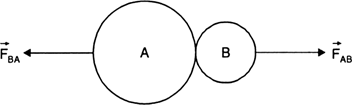
Fig. Action of Newton’s third law.
As shown in fig.,
If ![]() is the force exerted by body A on B and
is the force exerted by body A on B and ![]() is the force exerted by B on A, then according to Newton's third law,
is the force exerted by B on A, then according to Newton's third law,
![]()
We can see that the forces are equal and opposite.
According to the third law of motion, single force can never exist.
The forces always exist in pairs.
The two opposing forces are known as action and reaction forces.
But the forces of action and reaction always act on two different bodies.



