The velocity-time graph of a ball of 20 g moving along a straight line on a long table is given in Fig. 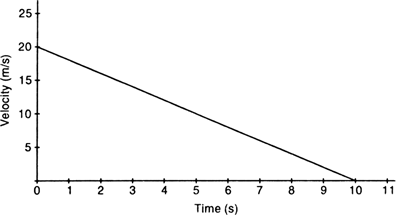
How much force does the table exert on the ball to bring it to rest?
Given,
Mass of the body, m = 20 g = 0.02 kg
From the given graph, we note that
Initial velocity, u = 20 cm/s = 0.20 m/s
Final velocity, v = 0 cm/s
Time taken, t = 10 - 0 = 10s
The force exerted on the ball is,
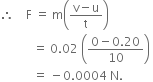
The negative sign shows that the friction force exerted by the table is opposite to the direction of motion of the ball.



