Give an illustration to show that a force can change the shape of an object.
Consider a spring attached to a rigid support at its one end, as shown in Fig.(a). 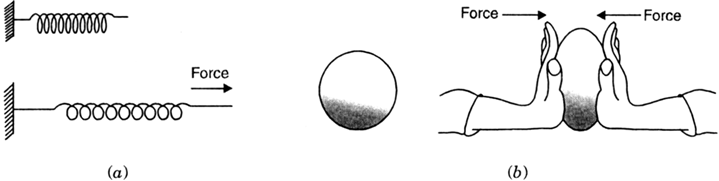
Fig.(a): A spring expands on application of force; (b) A spherical rubber ball becomes oblong as we apply force on it.
If we pull the free end of the spring, it gets elongated. Thus, on appying a force, a spring expands.
Similarly, if we hold a rubber ball between our palms and push the two palms against each other, we find that the ball is no longer round but oblong. See fig. (b). The oblongation of the ball is due to the application of the force.



