What are balanced forces? Give examples.
When the resultant of several forces acting on a body is zero, the forces are said to be ‘balanced forces’.
Balanced forces do not change the speed but changes the shape of the object.
Examples of balanced forces:
(i) If a bag full of books is held in hand steadily at a certain height from the ground, the resultant force on the bag is zero and so its position does not change.
(ii) Consider a wooden block lying on a table as shown in Fig.(a). 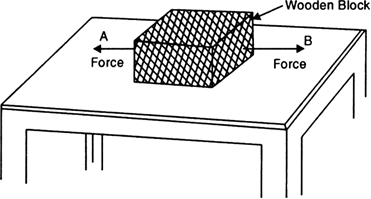
It has strings tied to its two opposite faces. /the wooden block move towards left, if the string is pulled at point A. If we pull at point B, it begins to move towards right.
But, if we pull from both, the sides with equal effort (and hence equal force), the block does not move.
The two forces have now balanced each other.
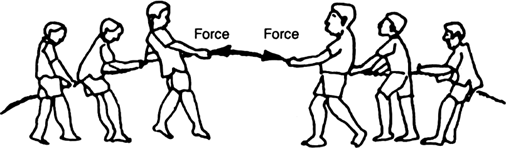
iii) In a tug-of-war, the rope does not move in any direction if the two teams pull the rope with equal effort.
The forces exerted by the two teams are equal and opposite and so get balanced.
This is illustrated as shown in fig. (b).