An object of mass 100 kg is accelerated uniformly from a velocity of 5 ms–1 to 8 ms–1 in 6 s. Calculate the initial and final momentum of the object. Also find the magnitude of the force exerted on the object.
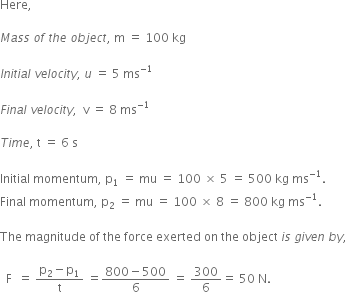
An object of mass 100 kg is accelerated uniformly from a velocity of 5 ms–1 to 8 ms–1 in 6 s. Calculate the initial and final momentum of the object. Also find the magnitude of the force exerted on the object.
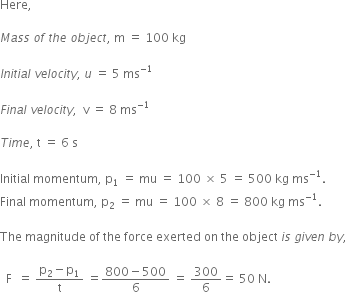
Write the steps you would use for making tea. Use the words—solution, solvent, solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate and residue.
Pragya tested the solubility of three different substances at different temperatures and collected the data as given below (results are given in the following table, as grams of substance dissolved in 100 grams of water to form a saturated solution).
|
Substance Dissolved |
Temperature in K |
||||
|
283 |
293 |
313 |
333 |
353 |
|
|
Potassium nitrate |
21 |
32 |
62 |
106 |
107 |
|
Sodium chloride |
36 |
36 |
36 |
37 |
37 |
|
Potassium chloride |
35 |
35 |
40 |
46 |
54 |
|
Ammonium chloride |
24 |
37 |
41 |
55 |
66 |
Pragya makes a saturated solution of potassium chloride in water at 353 K and leaves the solution to cool at room temperature. What would she observe as the solution cools? Explain.
|
Substance Dissolved |
Temperature in K |
||||
|
283 |
293 |
313 |
333 |
353 |
|
|
Potassium nitrate |
21 |
32 |
62 |
106 |
107 |
|
Sodium chloride |
36 |
36 |
36 |
37 |
37 |
|
Potassium chloride |
35 |
35 |
40 |
46 |
54 |
|
Ammonium chloride |
24 |
37 |
41 |
55 |
66 |
Find the solubility of each salt at 293 K. Which salt has the highest solubility at this temperature?
|
Substance Dissolved |
Temperature in K |
||||
|
283 |
293 |
313 |
333 |
353 |
|
|
Potassium nitrate |
21 |
32 |
62 |
106 |
107 |
|
Sodium chloride |
36 |
36 |
36 |
37 |
37 |
|
Potassium chloride |
35 |
35 |
40 |
46 |
54 |
|
Ammonium chloride |
24 |
37 |
41 |
55 |
66 |
Pragya tested the solubility of three different substances at different temperatures and collected the data as given below (results are given in the following table, as grams of substance dissolved in 100 grams of water to form a saturated solution).
|
Substance Dissolved |
Temperature in K |
||||
|
283 |
293 |
313 |
333 |
353 |
|
|
Potassium nitrate |
21 |
32 |
62 |
106 |
107 |
|
Sodium chloride |
36 |
36 |
36 |
37 |
37 |
|
Potassium chloride |
35 |
35 |
40 |
46 |
54 |
|
Ammonium chloride |
24 |
37 |
41 |
55 |
66 |
Explain the following giving examples:
Saturated solution
Mock Test Series