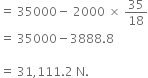A 8000 kg engine pulls a train of 5 wagons, each of 2000 kg along a horizontal track. If the engine exerts a force of 40,000 N. If the track offers a friction force of 5,000 N, then calculate:
(a) the net acceleration force;
(b) the acceleration of the train; and
(c) the force of wagon 1 on wagon 2.
Total mass of engine and 5 wagons, m = 8,000 + 5 x 2,000 = 18,000 kg
(a) The net accelerating force is given by,
F = Engine Force - Friction Force
= 40,000 - 5,000
= 35000 N.
(b) The acceleration of the train is given by, ![]()
(c) The force of wagon 1 on wagon 2
= Net accelerating force - mass of wagon x acceleration