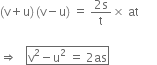Establish the relation v 2 – u2 = 2as, where ‘u’ is the initial velocity, ‘v’ the final velocity, ‘a’ the uniform acceleration and ‘s’ is the distance covered by the body.
Third equation of motion:
Let a body start with initial velocity u. After covering distance 's' under uniform acceleration 'a', its velocity becomes 'v' in 't' seconds.
Then, ![]()
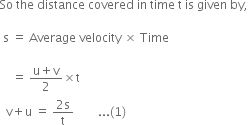
Now, using the first equation of motion:
v = u + at ![]() v - u = at ... (2)
v - u = at ... (2)
Multiplying equations (i) and (ii), we get