Describe the process to show that the dye used in blue/black ink is a mixture of two or more components.
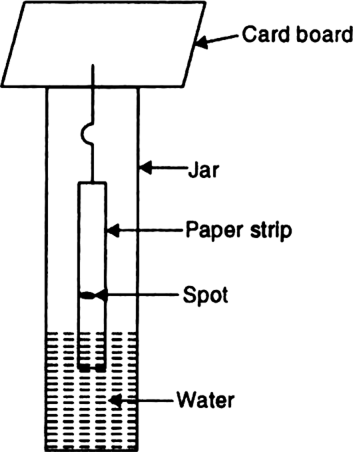
Describe the process to show that the dye used in blue/black ink is a mixture of two or more components.

Which separation techniques will you apply for the separation of the following?
Small pieces of metal in the engine oil of a car.
Which separation techniques will you apply for the separation of the following?
Different pigments from an extract of flower petals.
Which separation techniques will you apply for the separation of the following?
Butter from curd.
Write the steps you would use for making tea. Use the words—solution, solvent, solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate and residue.
Pragya tested the solubility of three different substances at different temperatures and collected the data as given below (results are given in the following table, as grams of substance dissolved in 100 grams of water to form a saturated solution).
|
Substance Dissolved |
Temperature in K |
||||
|
283 |
293 |
313 |
333 |
353 |
|
|
Potassium nitrate |
21 |
32 |
62 |
106 |
107 |
|
Sodium chloride |
36 |
36 |
36 |
37 |
37 |
|
Potassium chloride |
35 |
35 |
40 |
46 |
54 |
|
Ammonium chloride |
24 |
37 |
41 |
55 |
66 |
Mock Test Series