What are colloids? State their characteristics.
If the size of the particles of the solute (also called dispersed phase) is between 1 nm and 100 nm, then these are called colloids. Their solutions are known as colloidal solutions. The colloids exhibit the following characteristic properties:
(i) Brownian motion. Colloidal particles move at random in zig-zag paths like gas particles. This is called Brownian motion. This type of motion is caused due to the collisions between the particles of the dispersion medium and the colloidal particles.
(ii) Tyndall effect. When strong beam of light is passed through a true solution taken in a beaker placed in a dark room, the path of light through the solution is dark. But if the light is passed through a colloidal solution under conditions as above, the path of light through the colloidal solution becomes visible. This is called Tyndall effect. The colloidal particles become illuminated because they scatter the light falling on them in all directions.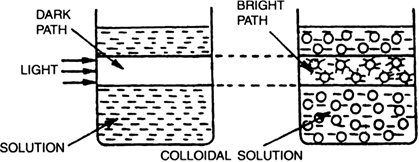
Fig. Tyndall effect.
(iii) Electrophoresis: When an electric current is passed through a colloidal solution, the particles move either towards the positive or negative electrode. This phenomenon is known as electrophoresis. By the direction of the movement of colloidal particles, we can know the nature of the charge on them.
Electrophoresis



