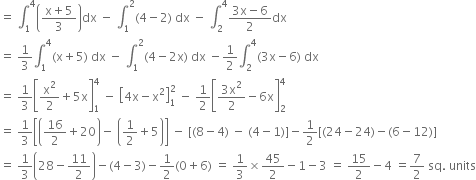Question
Using the method of integration find the area of the region bounded by lines:
2 x + y = 4, 3 x - 2 y = 6 and x - 3 y + 5 = 0.
Solution
The equations of the sides are
2 x + y - 4 = 0 ...(1)
3 x - 2 y - 6 = 0 ...(2)
x - 3 y + 5 = 0 ...(3)
Solving (1) and (2), we get
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solving (2) and (3), we get,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solving (1) and (3), we get,
![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]()
From B. draw BL ⊥ x-axis and from A. draw AM ⊥ x-axis.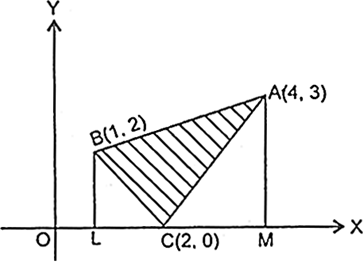
Required area = Area of ![]() = Area of region BLMA - area of
= Area of region BLMA - area of ![]() - area of
- area of ![]()