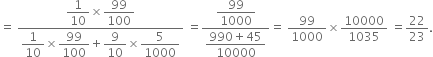Question
A laboratory blood test is 99% effective in detecting a certain disease when it is in fact, present. However, the test also yields a false positive result for 0.5% of the healthy person tested (i.e. if a healthy person is tested, then, with probability 0.005, the test will imply he has the disease). If 0.1 percent of the population actually has the disease, what is the probability that a person has the disease given that his test result is positive?
Solution
Let E1, E2, E be the events
E1 : ‘the person has the disease’
E2 : ‘the person is healthy’,
E : ‘test is positive’,
![]()
![]()
Required probability = ![]()
(By Bare's Theorem)