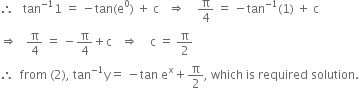Question
Find the particular solution of the differential equation
(1 + e2x ) dy + (1 + y2 ) ex dx = 0, given that y = 1 when x = 0.
Solution
The given differential equation is
(1 + e2x ) dy + (1 + y2 ) ex dx = 0 or (1 + e2x ) dy = - (1 + y2 ) ex dx![]()
![]()
Let I = ![]()
Put ![]()
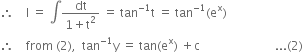
Now, x = 0, y = 1