Construct a triangle of sides 4 cm, 5 cm and 6 cm and then a triangle similar to it whose sides arc 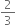 of the corresponding sides of the first triangle.
of the corresponding sides of the first triangle.
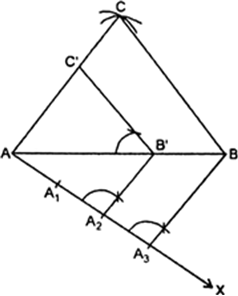
(i) Construct a ΔABC in which AB = 6 cm, AC = 4 cm, BC = 5 cm.
(ii) At A draw an acute ∠BAX below base AB.
(iii) Along AX mark off points A1, A2, A3 such that AA1 = A1 A1 = A2 A3.
(iv) Join A3B.
(v) From A2 draw A2B’ || A3B meeting AB at B’.
(vi) From B’ draw B‘C’ || CB meeting AC at C’. Thus, ΔAB‘C’ is the required triangle, each of whose sides is (2/3)rd of the corresponding sides of the ΔABC.
Justification :
[From (i)]
[By Basic proportionality theorem)





