Question
The coordinates of the points given in the following table represent some of the solutions of the equation 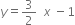
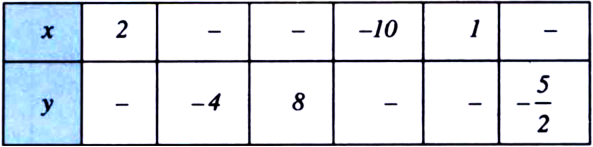
Find the missing values. Also find the coordinates of the points where the line cuts x-axis and y-axis.
Solution
![]()
When x = 2, ![]()
When y = -4, -4 = ![]()
![]()
When y = 8, 8 = ![]()
![]()
![]() x = 6
x = 6
When x = -10, y = ![]()
When x = 1, y = ![]()
When y = ![]()
![]()
![]() x = -1
x = -1
Hence, the completed table is as follows:![]()
For intersection with x-axis, put y = 0
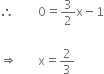
Hence, the point of intersection is ![]()
For intersection with y-axis, put x = 0![]() y = -1
y = -1
Hence, the intersection is (0, -1)



