Sponsor Area
Market Equilibrium
Explain the effects of 'maximum price ceiling' on the market of a good'? Use diagram.
A price ceiling is a government-imposed price control or limit on how high a price is charged for a product. Governments intend price ceilings to protect consumers from conditions that could make necessary commodities unattainable. It is the legislated or government imposed maximum level of price that can be charged by the seller. Since price ceiling is lower than the equilibrium price thus the imposition of the price ceiling leads to excess demand as shown in the diagram below.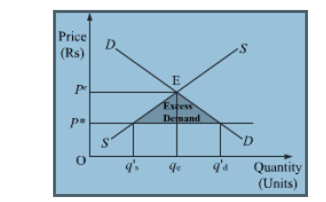
The following are the consequences and effects of price ceiling:
1) An effective price ceiling will lower the price of a good, which decreases the producer surplus. The effective price ceiling will also decrease the price for consumers,but any benefit gained from that will be minimized by the decreased sales due to the drop in supply caused by the lower price.
2) If a ceiling is to be imposed for a long period of time, a government may need to ration the good to ensure availability for the greatest number of consumers.
3) Prolonged shortages caused by price ceilings can create black markets for that good.
4) Due to artificially lowering the price, the demand becomes comparatively higher than the supply. This leads to the emergence of the problem of excess demand.
5) The imposition of the price ceiling ensures the access of the necessity goods within the reach of the poor people. This safeguards and enhances the welfare of the poor and vulnerable sections of the society.
6) Each consumer gets a fixed quantity of good (as per the quota). The quantity often falls short of meeting the individual’s requirements. This further leads to the problem of shortage and the consumer remains unsatisfied.
7) Often it has been found that the goods that are available at the ration shops are usually inferior goods and are adulterated and infiltrated.
Some More Questions From Market Equilibrium Chapter
Market for a good is in equilibrium. The demand for the good 'increases'. Explain the chain of effects of this change.
Market of a commodity is in equilibrium. Demand for the commodity "increases." Explain the chain of effects of this change till the market again reaches equilibrium. Use diagram.
Giving reasons, state whether the following statements are true or false.
A monopolist can sell any quantity he likes at a price.
A monopolist can sell any quantity he likes at a price.
Giving reasons, state whether the following statements are true or false.
When equilibrium price of a good is less than its market price, there will be competition among the sellers.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is simultaneous increase both in demand and supply of the good. Explain its effect on market price.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is simultaneous decrease both in demand and supply of the good. Explain its effect on market price.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is an 'increase' in demand for this good. Explain the chain of effects of this change. Use diagram.
What is minimum price ceiling? Explain its implications.
If the prevailing market price is above the equilibrium price, explain its chain of effects.
The demand of a commodity when measured through the expenditure approach is inelastic. A fall in its price will result in :
(choose the correct alternative)
(a) no change in expenditure on it.
(b) increase in expenditure on it.
(c) decrease in expenditure on it.
(d) any one of the above
(choose the correct alternative)
(a) no change in expenditure on it.
(b) increase in expenditure on it.
(c) decrease in expenditure on it.
(d) any one of the above
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





