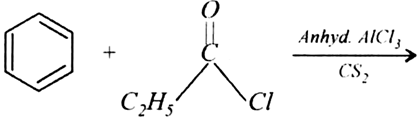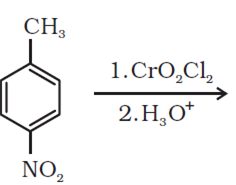b)
Distinguish between:
i) C6H5-COCH3 and C6H5-CHO
ii) CH3COOH and HCOOH
c) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CHO,CH3COOH,CH3CH2OH
Or
a) Write the chemical reaction involved in Wolff Kishner reduction.
b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction:
C6H5COCH3, CH3-CHO, CH3COCH3
c) why carboxylic acid does not give reactions of carbonyl group ?
d) Write the product in the following reaction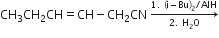
e) A and B are two functional isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and I2, isomers B forms a yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas isomer A does not form any precipitate. Write the formulae of A and B.

b)
(i)Heat both compounds with NaOH and I2, C6H5COCH3 forms yellow ppt of CHI3 whereas C6H5CHO does not.
(ii)Add ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate (Tollen’s reagent) to both the compounds, HCOOH gives silver mirror but CH3COOH does not.
C) CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH < CH3COOH
Or
a) 
b)C6H5COCH3 < CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO
(c) Because of resonance in the carboxylic group the carbonyl group loses a double bond character.
d) 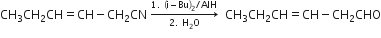
e) A : CH3CH2CHO B : CH3COCH3