How can you separate a mixture of primary, secondary and tertiary amines? Write chemical reactions involved in the process.
Hinsberg test is employed to separate primary, secondary and tertiary amines from a mixture. In this test the mixture of amines is treated with benzene sulphonyl chloride C6H5SO2Cl (Hinsberg’s reagent) followed by treatment with aqueous KOH (5%) solution and then shaken with ether in a separatory funnel.
(a) The primary amine reacts forming mono alkyl sulphonamide which is soluble in alkali forming a potassium salt which forms the lower aqueous layer.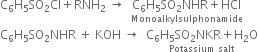
(b) The secondary amine reacts forming dialkylsulphonamide which is insoluble in alkali.![]()
The tertiary amines does not react at all.
Both dialkyl sulphonamide and tertiary amine go into the upper ether layer. While the monoalkyl sulphonamide remains in the lower aqueous layer. The two layers are separated, the aqueous layer containing the potassium salt of mono-alkyl sulphonamide is hydrolysed with concentrated hydrochloric acid when primary amine is regenerated as its hydrochloride.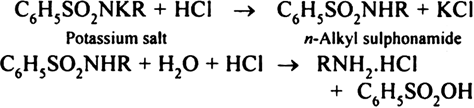
Primary amine is recovered from the hydrochloride by distillation with alkali.
RNH2.HCl+ KOH → RNH2 + KCl + H2O
The ether layer distilled when tertiary amine distills over. The residue of dialkyl sulphonamide is hydrolysed with concentrated hydrochloric acid when secondary amine is regenerated as its hydrochloride.
C6H5SO2NR2 +H2O + HCI → C6H5SO2OH + R2NH.HCl
The hydrochloride on distillation with alkali gives the free secondary amine
R2NH.HCl + KOH → R2NH + KCl + H2O



