Question
Explain the following terms: (i) Electrophoresis (ii) Coagulation (iv) Dialysis (iv) Tyndall effect.
Solution
Answer:
The movement of colloidal particles under an applied electric potential is called electrophoresis.
when electric potential is applied across two plantium electrodes depping in colloidal solution.
positively charged particles moves towards the cathode while negtive charge particles moves towards anode.

(ii) Coagulation. The precipitation of colloidal particles is known as coagulation. This is caused by the neutralization of charge on colloidal particles when an electrolyte is added to the sol.
(iii) Dialysis.It is a process of removing a dissolved substance from a colloidal solution by means of diffusion through a suitable membrane. Particles of true solution can pass through parchment paper or cellaphane membrane whereas sol particles cannot pass through these membrane.
A bag made up of such a membrane is filled with colloidal solution and is then suspended in fresh water. The electrolyte particles pass out leaving behind the colloidal solution.
Movement of ions across the membrane can be expedited by applying electric current through two electrodes. This method is very fast and is known as electro-dialysis.
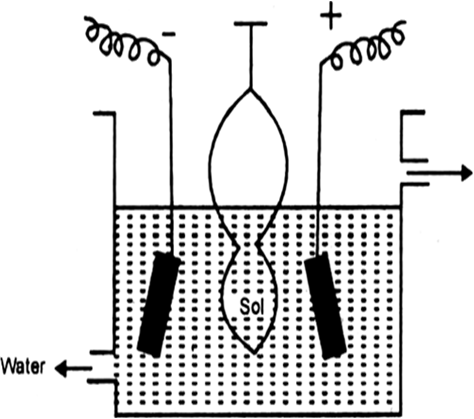
Fig.Electro-dialysis.
(iv) Tyndall effect: It is observed that when a beam of light enters a dark room, the dust particles in its path become clearly visible. When a strong beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution and viewed at right angles, the path of light shows up as a hazy beam or cone. This is due to the fact that sol-particles absorb light energy and then emit it in all directions in space. This scattering of light, as it is called illuminates the path of the beam in the colloidal dispersion.

“The phenomenon of the scattering of light by sol particles is called Tyndall effect”.
True solutions do not exhibit Tyndall effect.
The movement of colloidal particles under an applied electric potential is called electrophoresis.
when electric potential is applied across two plantium electrodes depping in colloidal solution.
positively charged particles moves towards the cathode while negtive charge particles moves towards anode.

(ii) Coagulation. The precipitation of colloidal particles is known as coagulation. This is caused by the neutralization of charge on colloidal particles when an electrolyte is added to the sol.
(iii) Dialysis.It is a process of removing a dissolved substance from a colloidal solution by means of diffusion through a suitable membrane. Particles of true solution can pass through parchment paper or cellaphane membrane whereas sol particles cannot pass through these membrane.
A bag made up of such a membrane is filled with colloidal solution and is then suspended in fresh water. The electrolyte particles pass out leaving behind the colloidal solution.
Movement of ions across the membrane can be expedited by applying electric current through two electrodes. This method is very fast and is known as electro-dialysis.

Fig.Electro-dialysis.
(iv) Tyndall effect: It is observed that when a beam of light enters a dark room, the dust particles in its path become clearly visible. When a strong beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution and viewed at right angles, the path of light shows up as a hazy beam or cone. This is due to the fact that sol-particles absorb light energy and then emit it in all directions in space. This scattering of light, as it is called illuminates the path of the beam in the colloidal dispersion.

“The phenomenon of the scattering of light by sol particles is called Tyndall effect”.
True solutions do not exhibit Tyndall effect.



