-
Call Us
+91 8076753736 -
Send us an Email
[email protected]
States Of Matter
The intermolecular interaction that is dependent on the inverse cube of the distance between the molecule is:
-
ion-ion interaction
-
ion-dipole interaction
-
London force
-
hydrogen bond
B.
ion-dipole interaction
ion-ion interaction is dependent on the square of the distance,
i.e, ion-ion interaction ∝ 1/r2
Similarly,
ion-dipole interaction ∝ 1/r3
London forces ∝ 1/r6
and dipole-dipole interactions ∝ 1/r3
superficially it seems as both ions interaction and hydrogen bonding vary with the inverse cube of the distance between the molecules but when we look at the exact expressions of field (force) created in two situations it comes as,
In the case of ion-dipole interaction: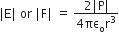
and, In the case of dipole-dipole interaction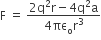
From the above it is very clear, the ion-dipole interaction is the better answer as compared dipole-dipole interaction i.e. hydrogen bonding.
Sponsor Area
Some More Questions From States of Matter Chapter
Which state of matter has a definite volume but no definite shape?
What is absolute temperature?
What is the absolute zero temperature?
Can absolute zero temperature be attained for a gas?
How pressure of a given sample of gas is related to absolute temperature at constant volume?
How is the pressure of a gas related to the number of molecules of the gas at constant temperature and volume?
What is standard (or normal) temperature and pressure (STP)?
What does SATP stand for? Define it.
What is the value of molar volume at STP?
Mock Test Series
Sponsor Area
 Wired Faculty
Wired Faculty



