Sponsor Area
Hydrocarbons
At 300 K and 1 atm, 15 mL of a gaseous hydrocarbon requires 375 mL air containing 20% O2 by volume for complete combustion. After combustion the gases occupy 330 mL. Assuming that the water formed is in liquid form and the volumes were measured at the same temperature and pressure, the formula of the hydrocarbon is:
-
C3H8
-
C4H8
-
C4H12
-
C3H6
C.
C4H12
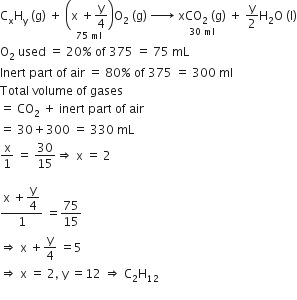
Some More Questions From Hydrocarbons Chapter
Out of n-pentane, isopentane and neopentane which has lower boiling point?
During the pyrolysis of alkanes C-C bonds break in preference to C-H bond. Why?
Define cracking.
What is the function of iodic acid in the iodination of alkanes? Can we use any other substance in its place?
What is alternation effect?
Arrange the following compounds in order of their increasing boiling points:
n-Pentane, n-Hexane, Ethane, 2-2-Dimethylpentane, 2-Methylpentane.
n-Pentane, n-Hexane, Ethane, 2-2-Dimethylpentane, 2-Methylpentane.
Why is light or heat necessary to initiate chlorination reaction of alkanes?
What are conformation or rotational isomers?
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series
Mock Test Series





