Question
Apply the law of mass action to a reversible reaction and state the law of chemical equilibrium.
Solution
Let us consider a simple reversible reaction in the state of equilibrium

According to the law of mass action.
Rate of the forward reaction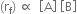
or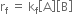
where kf is the rate constant for the forward reaction, [A] and [B] are molar concentrations of reactants A and B respectively.
Rate of the backward reaction (rb) ∝ [C] [D] or rb = kb [C] [D]
where kb is the rate constant for the backward reaction, [C] and [D] are molar concentrations of the products C and D respectively.
At equilibrium:
Rate of the forward reaction
= Rate of the backward reaction
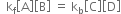
or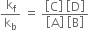
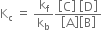
The constant is called equilibrium constant and has a constant value at a given temperature. Similarly, for a reaction
is called equilibrium constant and has a constant value at a given temperature. Similarly, for a reaction 

the above represents the complete expression for the law of chemical equilibrium. It may be defined as: For a reversible reaction at equilibrium, the ratio of the products of molar concentration of the products (substance formed) to the products of molar concentration of the reactants with each concentration term raised to a power equal to the number of moles of that substance in the balanced equation is constant at a given temperature.
According to the law of mass action.
Rate of the forward reaction
or
where kf is the rate constant for the forward reaction, [A] and [B] are molar concentrations of reactants A and B respectively.
Rate of the backward reaction (rb) ∝ [C] [D] or rb = kb [C] [D]
where kb is the rate constant for the backward reaction, [C] and [D] are molar concentrations of the products C and D respectively.
At equilibrium:
Rate of the forward reaction
= Rate of the backward reaction
or
The constant
the above represents the complete expression for the law of chemical equilibrium. It may be defined as: For a reversible reaction at equilibrium, the ratio of the products of molar concentration of the products (substance formed) to the products of molar concentration of the reactants with each concentration term raised to a power equal to the number of moles of that substance in the balanced equation is constant at a given temperature.



