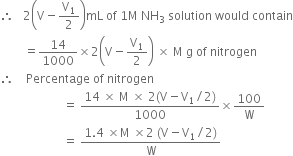How is nitrogen estimated in a given organic compound by Kjeldahl’s method?
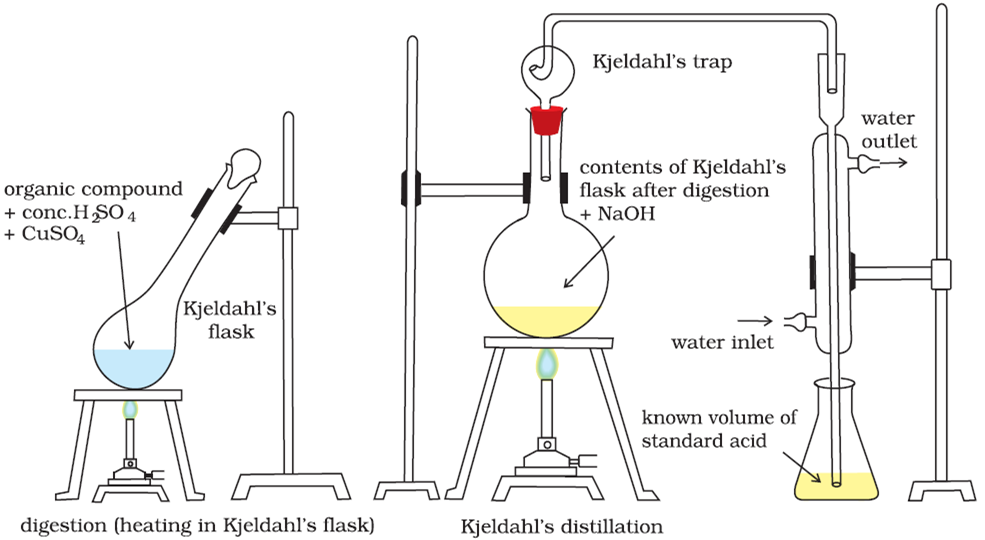
It consists in heating a known weight of a nitrogenous compound with concentrated sulphuric acid and a little K2SO4 and anhydrous CuSO4 (or mercury). Potassium sulphate raises the boiling point of H2SO4 and CuSO4 acts as a catalyst. Nitrogen present in the compound is quantitatively converted into ammonium sulphate. The resultant liquid is heated with concentrated sodium hydroxide. The ammonia gas thus liberated is absorbed in a known volume of an excess of a standard solution of acid. The acid left unused is titrated against a standard solution of alkali. Knowing the volume of acid used to neutralise ammonia, the volume of ammonia evolved and finally the percentage of nitrogen can be calculated.
Reactions involved are:
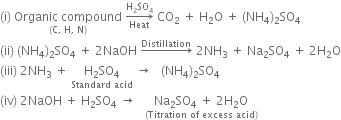
Calculations:
Let the mass of organic compound taken = Wg
Volume of standard
 taken
taken= V mL of 1 M solution
After the absorption of ammonia.
Volume of alkali required for the excess acid
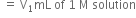
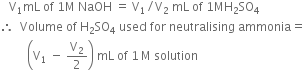

Also, 1000 mL of 1 M NH3 solution contains 14g nitrogen