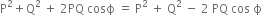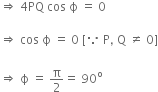At what height from the surface of earth the gravitation potential and the value of g are -5.4 x 107 J kg-2 and 6.0 m/s2 respectively? (Take the radius of the earth as 6400 km)
-
1600 km
-
1400 km
-
2000 km
-
2600 km
D.
2600 km
Gravitational potential at some height h from the surface of the earth is given by,
V =  ... (i)
... (i)
Acceleration due to gravity at some height h from the earth surface can be given as,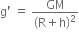 ... (ii)
... (ii)
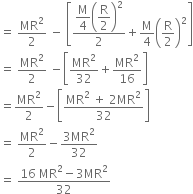
From equation (i) and (ii), we get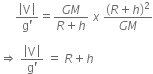 ... (iii)
... (iii)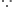 V = -54 x 107 J kg-2
V = -54 x 107 J kg-2
g' = 6.0 m/s2
Radius of Earth, R = 6400 km
Putting the values in Eqn. (iii), we get
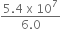 = R+h
= R+h
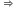 h = (9-6.4)x106 = 2.6 x 106 m
h = (9-6.4)x106 = 2.6 x 106 m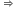 h = 2600 km
h = 2600 km





 . The coefficient of friction between the tyres of the car and the road is
. The coefficient of friction between the tyres of the car and the road is  . The maximum safe velocity on this road is,
. The maximum safe velocity on this road is,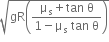
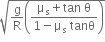
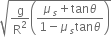
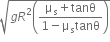
 and the coefficient of friction between the tyres of car and the road is
and the coefficient of friction between the tyres of car and the road is  .
.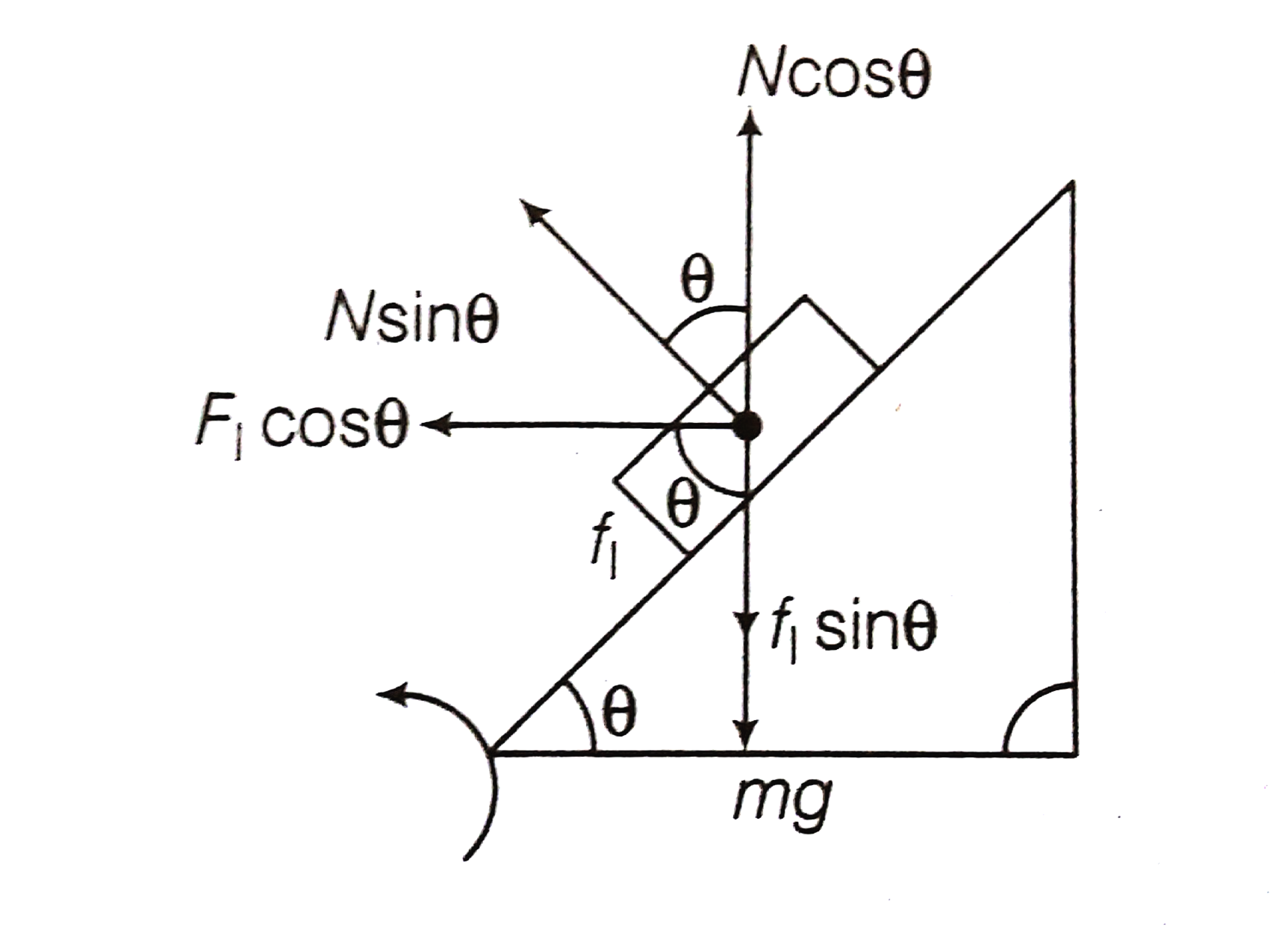
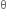 = mg + f1 sin
= mg + f1 sin 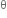
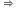 mg = N cos
mg = N cos 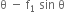 ... (i)
... (i)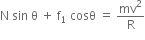 ... (ii)
... (ii)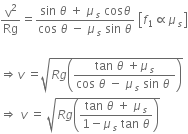
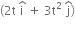 N, where
N, where  are units vectors along X and Y axis. What power will be developed by the force at the time (t)?
are units vectors along X and Y axis. What power will be developed by the force at the time (t)? +3t2
+3t2  ) N,
) N, are unit vectors along X and Y axis.
are unit vectors along X and Y axis.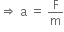
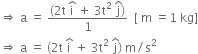
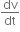

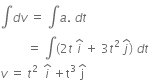
 + 3t2
+ 3t2 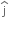 ).(
).(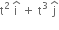 )
)
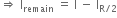
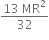
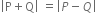
 ,
,