If energy (E), velocity (v) and time (T) are chosen as the fundamental quantities, the dimensional formula of surface tension will be
-
[Ev-2T-1]
-
[Ev-1T-2]
-
[Ev-2T-2]
-
[E-2v-1T-3]
C.
[Ev-2T-2]

Sponsor Area
If energy (E), velocity (v) and time (T) are chosen as the fundamental quantities, the dimensional formula of surface tension will be
[Ev-2T-1]
[Ev-1T-2]
[Ev-2T-2]
[E-2v-1T-3]
C.
[Ev-2T-2]

Sponsor Area
A particle of unit mass undergoes one-dimensional motion such that its velocity according to
V(x) = βx-2n where β and n are constants and x is the position of the particle. The acceleration of the particle as a function of x is given by
-2nβ2 x-2n-1
-2nβ2 x-4n-1
-2β x-2n+1
-2nβ2e-4n+1
B.
-2nβ2 x-4n-1
Given, v = βx-2n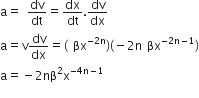
Two similar springs P and Q have spring constants KP and KQ, such that KP>KQ. They are stretched, first by the same amount (case a), then by the same force (case b). The work done by the springs WP and WQ are related as, in case (a) and case (b), respectively
WP =WQ ;WP> WQ
WP =WQ ;WP= WQ
WP > WQ ;WQ> WP
WP <WQ ; WP< WQ
C.
WP > WQ ;WQ> WP
Given KP>KQ
In case (a) the elongation is same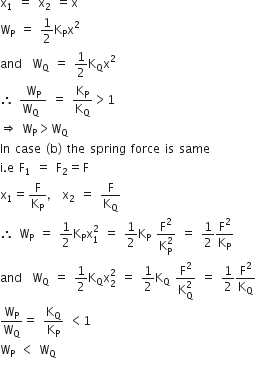
A block of mass 10 kg, moving in the x-direction with a constant speed of 10 ms-1 , is subjected to a retarding force F= 0.1x J/m during its travel from x = 20 m to 30 m. Its final KE will be
475 J
450 J
275 J
250 J
A.
475 J
From work energy theorem
work done = change in KE
⇒ W = Kf -Ki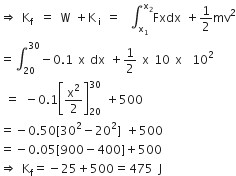
A particle of mass m is driven by a machine that delivers a constant power K watts. If the particle starts from rest, the force on the particle at time t is
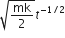



A.
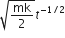
As the machine delivers a constant power
So F, v =constant = k (watts)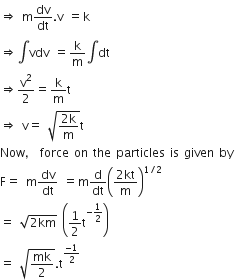
Sponsor Area
Mock Test Series