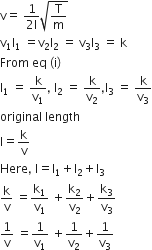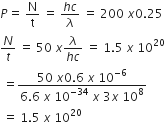When a string is divided into three segments of length l1, l2, and l3 the fundamental frequencies of these three segments are v1, v2, and v3 respectively. The original fundamental frequency (v) of the string is
-
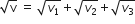
-
v = v1 +v2 +v3
-
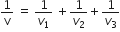
-

C.
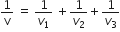
The fundamental frequency of string