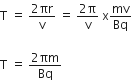An explosion blows a rock into three parts. Two parts go off at right angles to each other. These two are 1 kg first part moving with a velocity of 12 ms-1 and 2 kg second part moving with a velocity of 8 ms-1.If the third part flies off with a velocity of 4 ms-,its mass would be
-
5 kg
-
7 kg
-
17 kg
-
3 kg
A.
5 kg
apply the law of conservation of linear momentum.
momentum of first part = 1 x 12 = 12 kg ms-1
Momentum of the second part = 2 x 8 = 16 kg ms-1 '
Resultant monmentum
= [(12)2 +(16)2]1/2 = 20 kg ms-1
The third part should also have the same momentum.
Let the mass of third part be M, then
4 x M = 20