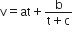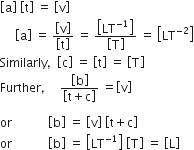For angles of projection of a projectile at angles (45° - θ) and (45° + θ), the horizontal ranges described by the projectile are in the ratio of
-
1:1
-
2:3
-
1:2
-
2:1
A.
1:1
For complementary angles of projection, their horizontal ranges will be same.
We know that, horizontal ranges for complementary angles of projection will be same.
The projectiles are projected at angles 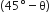 and
and  which are complementary to each other i.e., two angles add up to give
which are complementary to each other i.e., two angles add up to give  . Hence, horizontal ranges will be equal. Thus, the required ratio is 1:1.
. Hence, horizontal ranges will be equal. Thus, the required ratio is 1:1.






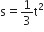 , where t is in s. Work done by the force in 2 s is:
, where t is in s. Work done by the force in 2 s is:

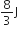

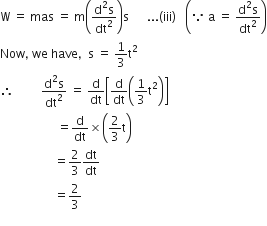
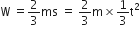
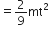
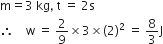
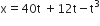
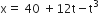
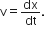
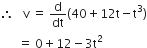
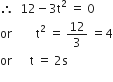
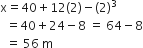
 where a, b and c are constants, The dimensions of a, b and c are respectively:
where a, b and c are constants, The dimensions of a, b and c are respectively: