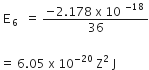The value of Planck's constant is 6.63 x 10-34 Js. The speed of light is 3 x1017 nms-1 . Which value is closet to the wavelength in nanometer of a quantum of light with frequency of 6 x 1015 s-1 ?
-
10
-
25
-
50
-
75
C.
50
Given, Planck's constant,
h= 6.63 x10-34
speed of light, c= 3 x1017 nms-1
Frequency of quanta
v=6 x1015 s-1
Wavelength, λ =?
We know that,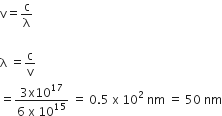






 certain conclusions are written. Which of them is not correct?
certain conclusions are written. Which of them is not correct?