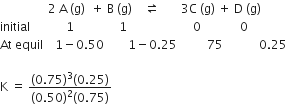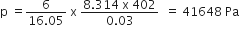Among the elements Ca, Mg, P and Cl, the order of increasing atomic radii is
-
Mg< Ca < Cl < P
-
Cl < P < Mg < Ca
-
P < Cl < Ca < Mg
-
Ca < Mg < P < Cl
B.
Cl < P < Mg < Ca
With the increase in the number of electron in the same shell, the atomic radii decrease due to increase in effective nuclear charge. However, atomic radii increases, as the number of shells increases. Thus, on moving down a group atomic radii increases.
The electronic configuration of the given elements is
Mg12 = [Ne] 3s2
Ca20 = [Ar] 4s2
P15 = [Ne]3s2 3p3
Cl17 = [Ne] 3s2 3p5
In Mg, P and Cl, the number of electrons is increasing in the same shell thus, the order of their atomic radii is
Cl <P < Mg
In Ca, the electron is entering in the higher shell, thus, it has the highest atomic radii among the given. Thus, the order of radii is
Cl < P < Mg < Ca